Today’s world is all about data, and bringing your data together is the heart of convergence marketing. When every department can access it, your customers stand to win through personalized and improved experiences. Let’s dive in to understand how convergence marketing benefits everyone and how to apply it successfully.
Traditionally, a business’s marketing, communications, and IT divisions are kept separate. These sections run independently of one another, interacting only when necessary.
This allows businesses to operate smoothly without having the burden of double and triple-check everything.

It’s a good approach, born from times when most management strategies were being developed. Times when keeping everyone up to speed meant sending paperwork back and forth between departments. It’s a lot of hassle, and efficiency dictated people should know only what’s needed for them to perform their jobs.
But we live in different times.
In today’s world, with technology allowing for instant communication and data sharing, this approach might seem outdated. Siloing your departments might be what’s always been done, but that doesn’t mean it’s the only way to go. That’s where a new approach comes in, called convergence marketing.
Keep reading to discover what potential it holds for your customers and company.
What does convergence marketing mean?
Convergence marketing is more of a philosophy than a strict step-by-step approach. In essence, it’s the art of merging your marketing, information, and design divisions in order to allow a unified message across all forms of marketing media you use.
The main idea of this approach is to place the customer at the center of all forms of communication, seeking to ensure that all messages they receive present a single, unified front.
This reduces the number of mixed messages the customer receives, allowing for greater brand recognition and trust to flourish.
Convergence marketing generally applies the most to digital or digital-supported forms of marketing. That’s because digital information can flow freely and seamlessly, as it’s retrieved from a database within milliseconds.
As such, attempting to converge marketing strategies that are mostly offline will be very difficult.
Convergence marketing vs. integrated marketing
A similar yet different term is integrated marketing.
Integrated marketing is all about coordinating marketing messages across different communication channels to increase brand awareness.
While this might seem identical to convergence marketing, this approach only considers the marketing department, ignoring all other aspects of the brand that might serve as touchpoints for customer communication.
It shares the same idea as convergence marketing but applies it on a smaller, more isolated scale. That being said, integrated marketing often happens naturally when you do convergence marketing, as you’ll likely factor in all communication channels.

What are the advantages of convergence marketing?
Now you may be thinking, this sounds like a lot of work, and that’s because it is.
Bringing separate departments of a business together is never easy, doubly so if you want them to be able to communicate in real-time.
If it’s that difficult to employ convergence marketing (which means it’s likely to cost a decent sum of money), why do it?
The benefits of convergence marketing tend to outweigh the costs if done correctly, as presenting a unified message on all fronts has numerous benefits. Let’s go over the most immediate ones.
Customer empowerment
By putting the customer at the center of your marketing strategy, you’ll be empowering them to act and provide feedback, giving them a voice in future decisions.
Any customer-centric marketing strategy takes in feedback, but where convergence marketing empowers customers is the linking of marketing and communications channels. Each piece of information collected by the communications team will be passed on to the marketing team and vice-versa.
This has the effect of not only increasing the customers’ voice within the organization as a whole, which allows you to tailor your marketing campaigns appropriately but increasing brand recognition overall.
While it might seem as though useful customer data is difficult to get, it’s been proven that two-thirds of consumers will willingly share their data with you if they think it will improve their overall experience.
They’re also willing to let you use first-party tracking cookies and other means of observing their online behavior if they think they’ll get something out of it.
In other words, convergence marketing is like symbiosis. Each party gives and takes, and both benefit overall.
Improved customer experience
Convergence marketing necessitates a shared database of information to which all sections of the business have access.
By creating this cross-transfer of information, various departments of your business will have access to all data collected on customers, enabling them to see previously documented interactions, and provide a better overall customer experience.
A Google report showed that up to 85% of digital customer journeys use more than one form of interaction with you. That’s a lot of data that you might miss if you’re relying only on information from one IP address.
With all available information on a particular customer, you will be able to learn what experiences they’ve had with you in the past, what approaches they respond best to, and even what might cause them to walk away satisfied.
Remember, engaging your customers is the best way to make sure they walk away happy!
Integrated communication between departments
Convergence marketing requires departments to collaborate, which means you need to have a robust communications system between them. Integrated communication isn’t so much an unintended benefit as a necessary part of convergence marketing.
Once the channels of communication are open, they can be used for more than they were designed for. Departments can share ideas and get feedback on them, ask for help from one another, etc.
Another factor is post-purchase customer service. Almost 60% of consumers would use social media to get this, but without information from the sales team on what’s been purchased, whoever is running the social media won’t be able to do their job.
Collaborations are also an option. With the traditional siloed form of organization, the different departments wouldn’t know about each other’s plans and, therefore, wouldn’t be able to offer assistance or request adjustments.
One of the greatest examples of inter-departmental collaboration in modern times can be found in Apple’s Transparency Report, designed to keep track of both government and private party data requests to Apple.
Apple’s aim here was to keep their customers reassured that their data was safe and wouldn’t be sold to third parties.
In order to achieve this massive task, Apple had to keep a record of any and all requests for data, the reason for such, and whether or not the request was granted.
This quite obviously involved their communications department. The collaboration also involved their legal team, who determined whether or not to release data in the face of law enforcement requests, and their information security team, who decided how to release the data.
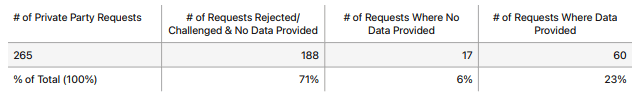
They pulled all information together and released it in the form of their Transparency Report, released annually. In the above table, taken from their 2021 report, you can see that over 70% of private-party data requests were rejected. Apple is practicing what they preach, being open and honest about its responses to data requests when needed.
Apple scored a major PR win with customers who want to keep track of their data and be reassured that Apple would only release it as a last resort. It’s arguably their greatest collaboration and one that perfectly exemplifies convergence marketing.
Instant access to information
Converging your departments necessitates placing information within a shared database. It also means that your data will take a standardized form and that anyone within your organization who has access can use it.
Imagine you’re a member of the marketing team who’s had an idea about using some of the latest designs in your new marketing campaigns. Without a unified database, you’d have to:
- Request the designs from the design team.
- Wait for a member of the design team to read your message.
- Wait for the design manager to okay sending the designs over.
- Wait for the design team to actually send the designs over.
Each of the above steps takes time, whereas with a unified database, you can simply hop into the relevant folder and pull the designs out for use.
Where and how can you apply convergence marketing in your business?
Convergence marketing isn’t something that you can apply overnight. It’s a slow and steady process that brings different sections of your business together, requiring careful preparation.
The simplest, and altogether the most sensible approach, is to alter each of your departments’ approaches little by little until they’re aligned with each other.
Once the processes and guidelines that each part of your business uses are similar, you can begin the sync, allowing them to work in harmony.
Let’s go over what each department needs to do to get the convergence ball rolling.

Marketing department
Convergence marketing, as the name suggests, is focused on marketing. It should come as no surprise in that case that the marketing department will be at the center of your efforts to converge.
When implementing convergence marketing, the first step in the process is to begin documenting and recording your marketing efforts within a database. That is, if you have not already done so.

The next step is to take a look at the way you store information, including but not limited to:
- Acronyms.
- Filetypes.
- Naming conventions.
- Database layouts.
- Access protocols.
These all need to be standardized into a form that the other departments involved in your efforts will be able to read and understand.
Once information is standardized it can be read by anyone who knows the syntax used, which should be provided to all other teams involved. Other teams may not necessarily use the same software as the marketing team, so you’ll need to take this into account.
You might be asking yourself, why is data standardization important? Surely anyone who needs to use the data can simply convert it into a form they can read.
The answer is two-fold.
Firstly, errors can crop up in translation. The data you end up with might not match the data you started out with, and it’s not feasible to manually check every piece that comes your way.
Secondly, your staff is only human. It’s inevitable that someone will forget to convert data, use the wrong conversion methods, etc.
If you think this is overstating the matter, please remember that NASA lost an entire Mars probe in 1999 thanks to someone forgetting to convert from inches to centimeters. Hopefully, any mistakes that crop up in your departments won’t cost $125 million and involve crashing objects into planets.
While standardized information is vital for all departments involved in the convergence efforts, it’s especially important for the marketing department.
And since marketing plays an integral part in your efforts, you should consider convergence within the department.
Internal convergence
Converging your marketing efforts can mean many things. Perhaps the most important aspect you should look at is converging your online and offline forms of marketing.
Due to their different philosophies, it’s common for businesses, especially larger ones, to silo these two forms of marketing into different teams so their operations flow smoothly.
Online marketing is a far more advanced approach, crunching big data from each particular consumer and personalizing ads and offerings based on behavior, interests, and more.
Offline marketing, on the other hand, needs to be far more general. It’s not that you can’t make offline forms of marketing more personalized; it’s that the amount of effort that it takes means it’s not always worth it.
In today’s world, attention spans are shorter than ever. It’s estimated that the average human’s attention span is just over 8 seconds, a drop of nearly 5 seconds from the year 2000. This puts the average human’s attention span at less than that of a goldfish!
This drop doesn’t come as a surprise, given how technology has sped up in the past 20+ years. With this information in mind, it’s more important than ever to grab consumers’ attention early on in your interactions.
That doesn’t mean you should ditch offline marketing efforts. Some can work brilliantly. Take the billboard below as an example.

It was created as part of a Minnesota anti-smoking campaign.
It’s a simple design, with only the website link on the billboard itself, but the pole beneath dressed up as a cigarette makes sure that we know the purpose of the advert.
The green color often associated with hospitals is the final nail in the board, subconsciously reminding the reader why they should consider getting in touch.
In short, the billboard has conveyed:
- What service is offered.
- How to best contact them.
- Why you should do so.
Online marketing can learn a lot from offline forms. Digital designers may be tempted to make elaborate and attention-grabbing content, but paradoxically it’s best to keep things simple even when you have a theoretically unlimited amount of space.
No one wants to keep scrolling forever, after all. It’s estimated that the average website user stays on a webpage for only 50 seconds, and that’s with an engaged audience, so you want them to take in as much information as possible in that time.
This is where the convergence of online and offline marketing comes into play, with the two learning from one another and leaning on each other. In all forms of media, you have to present information in a very efficient way. It’s not enough to simply make a consumer aware of your product. You need to tell them what it is and why it’s the best option for them to purchase.
The below images taken from IKEA’s website showcase how simple designs can convey a lot of information.
This image displays a sense of aesthetics that would make the viewer see IKEA positively while not being too complex or distracting from the point.
The second section, shown below, uses extremely simple outline images to get the point across, displaying all of IKEA’s services in a readable form.
Simple, easy-to-read marketing.
Communications
Communications refer to the part of your business responsible for communicating with outside parties. That’s anything from customer service helplines to writing emails to your shareholders.
In small businesses, this department might be merged with another or simply have its responsibilities spread across several other teams. Still, the principle behind convergence marketing extends whether you have a dedicated team or not.
Your communications department greatly benefits from convergence marketing, with the most obvious advantage being access to the other departments’ data.
With access to all the data your marketing department has collected on a particular customer, you’re better able to tailor your approach to them. This can extend to:
- The channel of communications.
- The tone used in communications.
- The complexity of the language used.
You might think that that’s all there is to it, but there are other benefits as well. Not only can the information you get improve your communications department’s operations, but collaboration with your other departments can provide benefits that neither could produce alone.
Take this creative approach from Capital One as an example.
The company was on the ball with their Capital One Cafes, a re-imagined form of banking where their branches doubled as cafes with co-working spaces and workshops.

Despite the fact that most banking is done online, there is still demand for in-person interaction when dealing with problems. Capital One saw this and decided to use its spaces as a means of connecting with the community better.
This strategy was the brainchild of combined marketing and communications thinking. Not only is the cafe a great marketing stunt, but it’s also a relaxed setting that consumers can use to communicate with the business without fear.
Going up to a teller screen can be intimidating after all, and many consumers are put off by the formality of the whole process. By removing the physical barrier between the bank workers and the customers, a more welcoming environment is created.
It’s doubtful that either department would have been given the go-ahead without collaboration. Altering your entire business strategy is extremely costly and risky, but with multiple departments backing it, the alterations went ahead.
Management
Finally, let’s talk about the management side of things, specifically the upper management. While there isn’t much to say regarding implementation, it’s easy to see the benefits, especially in terms of decision-making and cohesiveness.
It’s often said that the upper management doesn’t know nearly as much about the goings-on below them as they should. This is mostly due to how difficult it is to pass information and manage it in a centralized and standardized manner.
CEOs and COOs make the decisions, but how can they make them reliably when they aren’t getting the complete picture?
In the traditional approach, department directors report to their superiors, passing along different strategies, suggestions, and requests at once. Keeping track of all of that can prove difficult even for the most qualified managers.
By converging your marketing, there is a single, unified goal that the business wants to achieve. This means that anyone who makes these decisions can always fall back on that, rather than having to keep track of all the different strategies your business might be going after.
Convergence marketing is all about passing on information in a clear manner. Better information means better decisions, which make for better business strategies, and a more unified organization.
What tools can help enhance convergence marketing?
If you’ve read this far, you’re probably looking to apply convergence marketing to your organization. There are many ways and tools to go about it. So many that you may get overwhelmed at first.
To help make sense of all of this, we’ve prepared a list of the most useful tools and why they’re useful in tackling convergence marketing.
This isn’t an exhaustive list. It has to be on the general side of things, as each industry and context requires a different approach. So, if you think you have a better option, we encourage you to go for it.
Social media

Social media is a powerhouse of the current digital marketing age. It’s a tool that can create a lot of data for you to utilize, while also allowing for better interaction between your communications department and your customer base.
Social media communications is a tricky business, with even the most innocuous of comments being able to spark outrage or dissent among your viewers. By looping back real-time information into your marketing department, you will be able to mitigate any crises.
This is where social media monitoring comes in. Social media monitoring software can assist you in keeping track of your online statistics, flagging any urgent or suspicious data, and allowing you to give feedback and responses to questions rapidly.

The software is fairly new but has already made great strides. Some countries have even used it to monitor the accuracy of news shared on social media sites, with the aim of keeping their population informed when electing their new leaders.
In short, social media can be used as both a form of marketing and a form of communication, sometimes simultaneously.
The platform you use will depend on your market, target demographics, etc., but all share the advantage of global reach. Their downsides are also similar, with rapid responses and careful monitoring being crucial.
Mailshots
Mailshots, also called direct mail marketing, is the art of using mass production of a single advert to market to large numbers of consumers at once. Typically, the term has been used to refer to letters or leaflets you send through the post, but it is also applicable to email marketing.
The advantage of convergence marketing when using email mailshots is immense.
You can combine clicks and conversion statistics, along with other forms of data you’ve collected on customers to further personalize communications. Something you wouldn’t see in a siloed system.
And it’s a big deal, as segmentation and personalization are by far the most effective email strategies.
Consider the following scenario – a customer is after a specific brand of eyeliner, so they send an email to a store, asking if they have it in stock.
If your departments are siloed, the marketing department won’t know about this instance, and future newsletters and promotions will be less relevant for that person.
With your marketing and communications departments converged, this information will be communicated between them, allowing for it to be used in future personalized marketing efforts. The customer gets more relevant content, and you get a happier customer. Everybody wins.
To sum it up, mailshots are all about information. The more relevant you can be, the greater their chance of paying off. Keeping the flow of information open between departments means everything can be considered, not just what the marketing department has immediate access to.
Apps
When you create an engaging app for your brand, customers are more likely to use it for browsing, purchasing, and interacting with your company.
This gives you heaps of data about your customers in a simple and efficient manner. It’s especially true with apps as they’re usually linked to an individual account, leaving less margin for errors.
Another great thing about apps is they can be heavily personalized according to the data you just collected. Whether that’s to do with how the content in your app is laid out or specific times you’d like to use push notifications. There are even capabilities to change the design with AI-generated art, though these processes are still in the early stages.
All in all, apps are a sandbox for you to create your perfect customer contact point.
Cloud software databases
To move information between the different sections of your organization, you will need a database of some kind. In essence, each division needs to know what the others are doing and why they’re doing it. This prevents your sections from conflicting or producing mixed messages.
Cloud software is a particularly efficient method to use, with many tools to choose from. The main players are SalesForce, PipeDrive, and Zoho. Your choice will mainly depend on your organization’s:
- Size.
- Goals.
- And ability to implement technology.
Let’s go through a list of the benefits that cloud software can provide and discuss why they’re superior to other options.
Scalability
If you’ve ever used a flash drive or similar device to store your files, you know that they can very quickly become full. Data takes up space, and the amount of data you collect won’t always fit into the storage space you’ve allocated.
If you’re using traditional data storage means, you’ll need to physically go out and obtain more storage space, install it, link it to your data collection software, etc.
All that takes time, time in which valuable data will be lost. Cloud-based services offer expansion as your organization’s data storage needs grow. Perhaps more importantly, you can also decrease the capacity when you see a drop in your needs.
Cost-effectiveness
Cloud software is a far more cost-effective solution than traditional forms of information storage.
For one, you don’t have to store the data yourself in a physical location which would come with maintenance costs. You also don’t have to maintain and replace the storage drives every few years when the technology moves on, which is quite costly.
Another factor that bears mentioning is the time cost of duplicating files, emailing them to relevant people, and of those people downloading them. This might not seem like much, especially with smaller files, but when this process happens thousands of times a day, it starts to add up.
Easier collaboration
As mentioned before, the instant transfer of information between different people greatly benefits cloud software. However, the ability to collaborate goes further than that.
In traditional collaboration, one person might send a draft to a second, who suggests edits and sends it back. Then, if the first person doesn’t like some of those edits, they would suggest something else.
This takes time, causes great delays in projects, and is very inefficient overall. The key issue here is that each person cannot see what the other is doing until the edit is complete, and if they disapprove of it, that’s time and energy (and money) wasted!
With cloud software, the projects can be hosted online in a place that both participants in this hypothetical example can see. Each edit can be reacted to live as it is being done, saving time and effort in both parties’ cases.
Enhanced data security
Physical means of data storage aren’t the most secure. Once a connection is made, it’s very easy for a hacker to steal data and very difficult for you to stop them without physically severing the link to your server.
Cloud computing offers a unique opportunity in the data security world. Since your providers will necessarily have great data security measures in place (that’s their entire point), your customers can rest safe and easy knowing that their data won’t be stolen.
Cloud software is necessarily shared over multiple parties, which needs to be transmitted in real-time. This makes it an ideal candidate for blockchain security measures, which are considered almost unbreakable.
While data can be extracted from an external source, doing so requires the consent of all parties involved, so hackers would have to go the extra mile. Furthermore, a complete block in the chain cannot be altered, making most run-of-the-mill hacking methods ineffective.
Wrapping up
It’s not always easy to switch to new methods of thinking, but converged strategies are the future as customers are expecting a more personalized approach.
Convergence marketing ensures your customers will get it, as each department will be able to fetch, understand, and send data from across the company.
The next step would be to measure how customers feel about your new approach. Luckily, it’s something you can measure via advanced tools that provide sentiment analysis, providing valuable insights for your business. Read more about it here.
 All
Articles
All
Articles Email
Analytics
Email
Analytics






































