When creating a product, you can’t just spitball it. You need to take the time to create something that customers will actually want, and that is a better option than what they currently purchase. A product development strategy will assist you in finding your ideal product-market fit, and winning over customers from competing brands by providing a superior option.
What is a product development strategy?
You might have heard of the terms “new product development” or “new product development process” – while these are definitely important when creating a new product, they aren’t precisely what we’re talking about today.
A product development strategy is the direction that a new product release takes, from its market position to its overall demographic targeting process.
It’s a catch-all term that includes everything that takes place between having an idea for a product and actually putting it on the market.
The key takeaway here is that while new product development has to do with the actual act of creating a product, the product development strategy covers this and the steps needed to turn it into a viable, marketable product.
TCGen, which specializes in product development, has created a brilliant checklist that summarizes what a product development strategy is useful for, so take a look below.

So you might be thinking, if I’ve already implemented the new product development process, why do I need a product development strategy? After all, couldn’t I just take the end result and apply the same principles?
Well, you could. However, no business exists in a vacuum.
The fact of the matter is that some products aren’t just made for the sake of making good products that make money. They have another purpose. To gain a competitive advantage within the market, keep the company relevant, and claim a foothold that wouldn’t be available later.
It’s no coincidence that a new Xbox launches around the same time a new PlayStation does. Both companies can’t afford to concede market share to each other (Unless you’re Nintendo, and then you can do whatever you want).
Alternatively, businesses can patent & sell products simply so the competition can’t. Both Xbox and PlayStation have a long history of exclusive games, many of which were made by 3rd party companies.
The lesson here?
In the world of business, it isn’t enough to have a good product. You can still be undercut, out-advertised, and out-sold by another product if you don’t play it right.
That is to say, if you don’t have a good product development strategy.
What benefits can a product development strategy bring?
Okay, this sounds great in theory, but how do I apply it to my products? Fair question.
We touched briefly on why a product development strategy is important in the last section, but now it’s time to talk about tangible benefits.
So, what are some benefits of having a product development strategy?
Keeping an eye on the big picture from the start
When you have a product development strategy, you know exactly what it is you’re trying to achieve.
That might sound like common sense but bear with me here.
Let’s say you’re making a line of clothing, and your big-picture aim is to introduce hypo-allergenic fabrics that you can market to customers with sensitive skin.
Now, if you simply tell your design team that you want a certain set of clothing, e.g., pants, shirts, etc., from pure cotton, all they know is the letter of the instructions, not the spirit.
Nevertheless, they get on with it and have a working set of prototypes produced.
So the day comes for them to produce their designs, and lo-and-behold, they’ve used a dye that renders the line completely unusable by people with sensitive skin.
So what now? Well, they’ve got to go back to the drawing board with more precise instructions.
When you have an overarching aim, you need to keep all of your teams informed so they can create products that fit the spirit of your aims, not just the letter.
A product development strategy does exactly this, aiming to focus on the product’s placement and market position every step of the way.
Aligning cross-functional teams
When you run a business that creates products, it’s expected that you’ll have more than one team working on different steps of the process.
Those involved in product creation aren’t necessarily the ones who will be manufacturing it, and vice-versa. Thus, when creating a new product with a specific aim, you need to be keeping everyone on the same page if you want things to run smoothly.
Easier said than done.
Sometimes there are factors that one team is aware of, but the other is not, making the entire process grind to a halt when a plan is produced that simply doesn’t work under current limitations.
For simplicity’s sake, let’s take the example of the clothing manufacturer above again.
Your design team has managed to avoid the issue with dyes and has created a sensible prototype. And so, they decide to pass it on to the manufacturing team to produce.
However, you run into yet another roadblock.
You see, the supplier of the dye that you’ve selected has had some bad press, and the dye itself isn’t considered that reliable by those who find hypoallergenic clothes a necessity.
Now, anyone on the marketing team could have told you this. It’s their job to know the ins and outs of the current market, and they could have saved you from having to loop back again if only you’d communicated.
Product development strategies include communication aspects like these, using the big-picture focus to bring in new information when it’s needed.
Kellogg’s championed their traditional cereals such as Cornflakes, Froot Loops, and Frosties for decades, but with times changing and consumer preferences shifting, they’ve widened their reach by acquiring more diverse options to keep their customers happy.
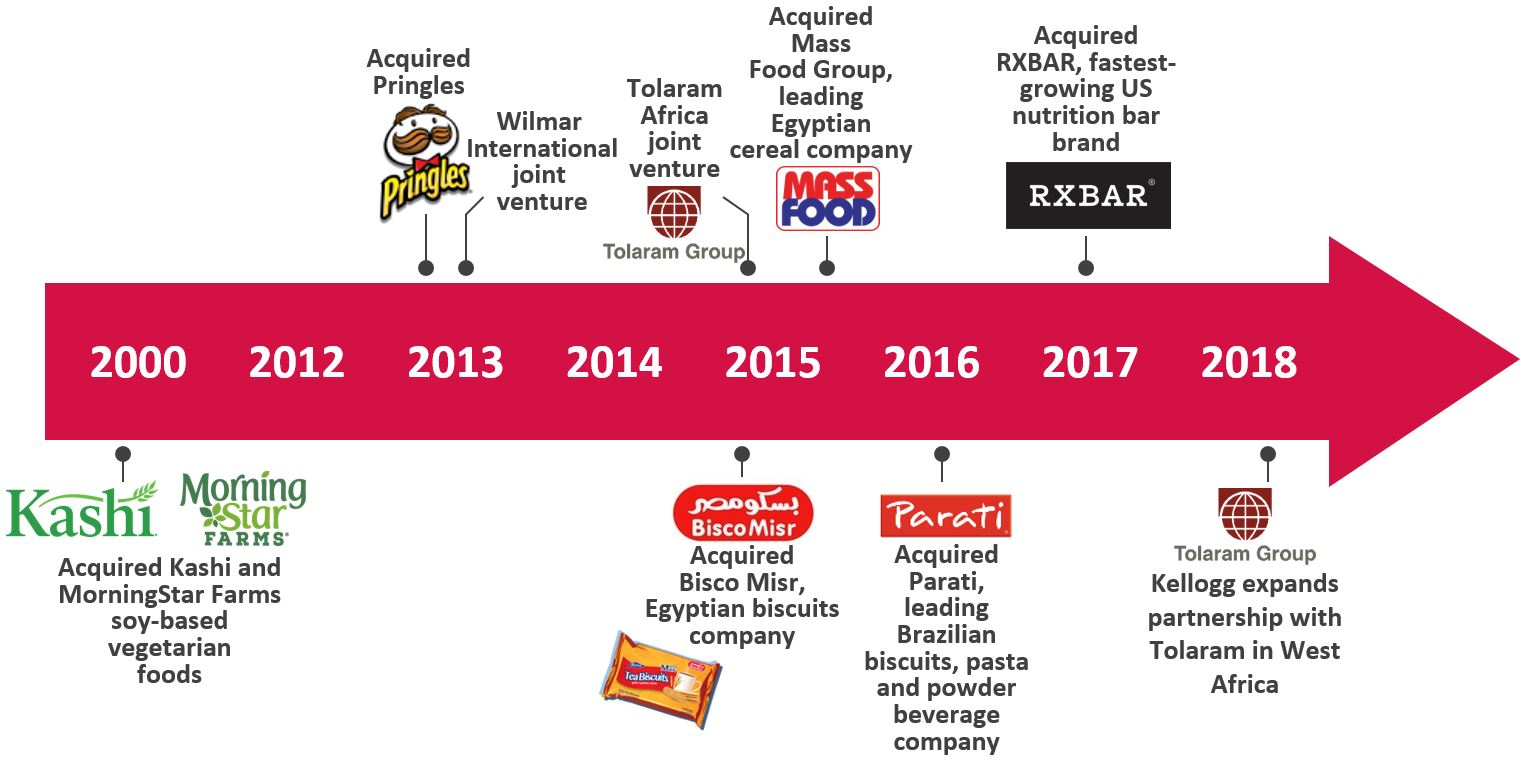
Feedback & guidance loops
Both of the above are examples of a business that’s missing feedback & guidance loops.
Feedback & guidance loops are lines of communication in which advice is passed on from further down the chain back to the product design team. By keeping themselves in the loop, delays and design errors can be avoided, and the process runs more smoothly overall.
Of course, these loops aren’t limited to being relevant to the design team.
All teams involved can benefit from them to some extent, even if the most obvious examples involve product design.
The big-picture approach requires, well, keeping the big picture in mind at all times.
And if factors change in one area, it’s going to have a knock-on effect that might alter your overall approach.
Efficiency
Lastly, let’s talk about efficiency.
The ultimate goal of business is to bring in revenue & make profits.
Now, this obviously means that you need a decent amount of sales, but there’s another side to it too. Costs.
You can have the most incredible products ever created, but if the costs of design are too high, then you’ll spend years in the red before ever being profitable.
That’s not to say that you can’t plan to be in the red, but it needs to be done carefully. Plenty of businesses thought that they were in the clear, only to be blindsided by the COVID-19 crisis in 2020.
What I’m trying to say is that the future is uncertain, and you need to be able to bounce back. Sinking into the red with a lengthy, inefficient product development process is precisely the opposite of that.
See, a lot of the time, your manufacturing costs can’t really be altered without affecting the quality of your products.
Your costs of sale, packaging, delivery, advertisement, and the like are often relatively static, especially if you use a third-party platform like Amazon or Etsy to sell.
So, when those two types of cost are static, and you need to lower your numbers, what do you do?
You improve your product development strategy, improve your efficiency, and decrease the amount of time & money it takes to develop a new product.
Every factor we’ve talked about thus far has been leading up to the ultimate goal of product development strategies; to make the process smoother and less costly to go through.
The 3 types of product development strategy
Rewinding back, let’s look at what a product development strategy is again before jumping right into the types you can have.
Product development strategies are all about aiming for sales. They’re all about trying to create & develop your new products in such a way that they’ll not only be great, but marketable.
You can have the greatest volcano-proof diving suit ever made, for example, but if no one will buy it, then from a business perspective, it’s a dud.
With that in mind, the types of product development strategies you can have are largely dependent on your marketing tactics.
Let’s take a look at the three most common types.
PDS type 1: Premium
When I think of premium, my mind jumps to brands like Louis Vuitton and Porsche.
What do these brands all have in common? Well, they’re high-end brands that market their products as luxuries, as things to aim to achieve.
They’re brands that enjoy high brand equity, with their products making people go “wow.”
These brands aim to be right at the top of the market, selling small numbers of products but at high prices. That way, they make a lot of profit per unit and increase their revenue overall.
There are downsides, though.
For one, costs are higher than average. This is expected, as you use “limited-edition” or “high-quality” materials in your products to make them more desirable.
Often, these materials are entirely superfluous to the nominal function of the product, such as diamond-encrusted handbags, but you could say that their purpose is to show off.
Remember, these are luxury products. Most drivers wouldn’t need a car that goes 250 mph and wouldn’t think about it when deciding to buy one. They’d just think about what can get them from A to B.
Someone looking for a luxury car, on the other hand, probably has the time and money spare to take it to a race track or onto a highway where such speeds are allowed, thus making such a feature relevant.
Further, luxury brands are very difficult to establish.
Unless you’re entering an entirely new market where almost all products were created recently, akin to Apple when establishing themselves in the PC industry, there are probably going to be big-name brands there already that won’t like you muscling in on their territory.
Keep in mind that often these brands have a long and proud history.
Many European and Asian brands date back centuries and take their longevity as a badge of honor. It’s taken as a standard of quality that they’ve been able to operate for so long and still stay in business.
The Genda Shigyō company that provides traditional Japanese gift wrapping has been running since 771! Just imagine trying to go up against that kind of established name!
There’s also the factor of a diminished customer base. It’s a fact that most Americans can’t afford luxury goods.
Fewer potential customers mean that every sale matters. Every sale lost matters even more. It’s vital to keep your quality high and your customers satisfied if you want to keep operating with this type of strategy.
PDS type 2: Budget
Entirely on the other end of the scale, we have the budget strategies.
These types of strategies follow the idiom “quantity over quality” to the extreme. In essence, by making very small amounts of profit on each sale but making lots of sales, you increase your profits.
And a low-cost product is far more likely to be bought by those who make choices on the basis of price alone, meaning a bigger reach for it.
Budget products are often thought of as low-quality, but this isn’t always the case. In this type of product development strategy especially, you keep your profit margins low to keep prices down rather than using cheap materials.
Remember, being a budget option does not mean you are cheap. It means you’re comparatively cheap when you consider the market as a whole.
A great example of this dichotomy is the smartphone industry. The cheapest new model will still set you back at least $50-100, not exactly budget.
Of course, if you do use cheap materials, you can lower your prices further and present yourself as a truly budget option, but that’s at the extreme end of the scale. The vast majority of products are not created to be cheap alternatives since consumers expect some measure of quality.
A phone that can barely load WhatsApp would probably sell poorly, after all.
There are some cons to this strategy.
You can quickly stray from low profit to no profit if your circumstances change. The difficulty with positioning yourself in this area comes with constantly having to monitor your operating costs, as even the tiniest increase will be a blow to your profits.
There’s also the factor of coming across as too cheap.
Generally, consumers are suspicious of products that are cheaper than others, even if reviews say that quality is consistent. It’s expected that certain types of products cost certain amounts, and any strategy that prices under this can be dismissed as being tacky.
Overall, this type of product development strategy is tricky to do but can perform wonderfully.
PDS type 3: Competitive
We’ve talked about the two extreme strategy types, but those are what they say on the tin, extremes. The vast majority of product development strategies fall somewhere in between, even if they do lean one way or the other.
Right in the middle of budget & luxury goods, you have competitive goods. These are products that have moderate profit margins and aim to sell a moderate amount of units.
How do you define moderate? A moderate price is determined by the average prices of that particular market as a whole. In other words, you price your product so it might be considered by the average consumer, keeping the quality consistent with what they’d expect for that price.
Let’s look at an example to make it clearer what this means.
When you think of high-end coffee, you might think of imported Jamaica Blue Mountain. On the other hand, if you want a low-budget option, you might settle for Dunkin’ Donuts’ own brand.
In the middle of these options sits Starbucks. Not too pricey and not low-quality. A good, reliable coffee shop that serves millions daily.
Starbucks occupies the competitive slot in this case, with their coffee being of a good enough quality to be called pleasant while keeping their prices low enough that they’re not a luxury brand.
Starbucks exemplifies the reason why most products are planned out to follow this route. You have the possibility of reaching almost all consumers, whether as a cheaper alternative to their luxury goods or as an upgrade from their usual once-in-a-while.
Your pricing strategy means that you make a decent amount of profit on each sale and aren’t that vulnerable to fluctuations in material costs or consumer tastes changing.
So what’s the catch? Why would anyone choose a different strategy than this, you might be asking?
Well, that’s precisely the reason. If everyone is aiming for this place in the market, then you’re simply one of a dozen.
Think of the last time you bought lightbulbs. Did you choose a specific brand, or did you just grab the first pack you saw on the shelf with a decent enough rating? Probably the latter.
When the market is saturated, you’re going to have a hard time establishing yourself as anything more than a face in the crowd. The reasons that brands want to choose this strategy are, paradoxically, the reasons that they can’t.
Not every coffee drinker goes to Starbucks, just as not everyone buys the same brand of shower gel. People buy what they’re used to, and unless you’re entering a market with something new and exciting, you’re simply going to fade away into the background.
Internal and external product development strategies – what’s the difference?
Now that we’ve talked about the different types of product development strategies, it’s time to take a brief note of… different types of product development strategies. ????
Hold on, this isn’t just a rehash of what we just spoke about, but something different entirely.
When you’re creating a new product, there are two different ways you can go about it. First off, you can utilize resources that you already possess, or you can look for possibilities that exist outside of these.
That’s what we call an internal vs. an external product development strategy.
Internal product development strategies
Internal product development typically refers to creating new products out of existing ones. That might be a personalized variant, a new and improved version of your product, or simply taking the ideas that exist within a product and applying them in new ways.
If you’re a smaller business or a start-up, you may find it hard to employ internal product development strategies since it’s possible you’ll lack the necessary resources. Look to the next section for how you might go about strategizing.
A common way for software companies to develop using internal product development is by acquiring smaller companies that produce complementary software, then combining them into a single package. This way, they can utilize their existing resources, which is far cheaper than creating new ones, and sell again as a new product.
Internal product development has several advantages, notably that you’ll already be established and can use the marketing from previous products to your advantage.
When Apple releases a new iPhone variant, for example, it’s always with the caption “the new iPhone” or “the upgraded iPhone” to allow consumers to subconsciously associate them with the success of previous versions.
Overall internal product development strategies are cheaper, easier to implement, and run far more smoothly on average since you probably know what you’re doing in this area.
On the flip side, there’s only so much you can do with an internal strategy since you’re limited by what you already possess. If you want to really innovate, you need to create an external product development strategy.
External product development strategies
External product development strategies are about creating something new. Something that your organization has never delved into before. This can be entering a new market, expanding into another country, etc.
External product development is a double-edged sword, however.
There are great rewards to be had with creating truly new, innovative products. Technological progress comes from external development, with giants like Thomas Edison & Nikola Tesla daring to be creative and develop something new.
However, this also comes at increased costs. After all, acquiring new assets takes funds, time, and effort, none of which are free.
When you create a new product using an external strategy, you could end up revolutionizing the future of electricity by patenting multiple electronic devices like Edison.
On the other hand, you could run out of money trying to build Wardenclyffe Tower like Tesla. The tower stood as a monument to human progress. However, it came at an extreme cost that couldn’t be recouped.
After all, it’s not enough in the world of business to simply innovate, you need to do it in a way that makes money and keeps your investors happy.
4 stages to creating a product development strategy
If you’ve read this far, you probably want to know how to go about creating a product development strategy.
To create one, you just need to follow the steps below. That’s it.
Go. ????
Stage #1: Defining your vision
First, you need to define your vision. This harkens back to our earlier discussion on the types of product development strategies you can use.
There are two questions that you can ask yourself when deciding what type of strategy is best.
- Do you want to be a budget option, a luxury option, or a middle-of-the-road?
- Do you intend to create something entirely new or to derive from existing assets?
To answer these, you need to have an idea of what you want to develop already in mind. Without this starting point, the entire plan falls apart.
Luckily, you can start with even the most ridiculous ideas. At this point, you’re not putting any material costs into the process, just time.
If you think your idea is too ridiculous, remember that someone once put their hand up in a board meeting and suggested a movie featuring “a tornado made of water with sharks in it.”
And it got sequels too!
Once you have your idea, you can start applying the potential options to it and seeing if they work.
Sometimes, you simply won’t be able to think of a place to market an idea, and that’s okay! Just file it away and move on to the next one until you find a concept you’re certain can fit one of these options.
Stage #2: Developing a strategic plan
Once you have your concept, it’s time to lay out a plan for how to create it.
The process of product creation can be as straightforward as designing a 3D file to send to a machine or as complex as mapping out a piece of software. Either way, it’s important to plan how you’re going to create it.
The strategic plan isn’t a step-by-step for how to produce your product. That comes later. Essentially, this is the process by which you link vision and reality, taking your concept and applying the first touch of real-world principles until you have a rough guide for how to begin.
The key idea here is to touch upon the real-world factors you’d need to consider, laying them out for future reference. It’s all about large strategic steps that might seem vague but are definitely necessary.
Remember, strategic plans aren’t the final word. They’re rough guides for how you want to go about your operations, with the actual details up in the air until they’re finalized. After all, you can’t predict how supply chains might look two years from now, so why finalize it right away?
Stage #3: Building a roadmap
Remember how we mentioned the step-by-step guide? This is it.
A product roadmap takes the broad steps of the strategy and breaks them down into recognizable, realizable steps. These are often built up over time and can be highly technical.
A roadmap is essentially a guide for how you will be bringing your product concept into being. It connects budgeting, assets, decisions that you need to make, and more.
When creating a roadmap, it greatly helps to keep things modular.
You might be thinking, what? Haven’t we just been talking about how important it is to keep everything running together?
So, when I say modular planning, I mean keeping every aspect of your roadmap separate yet connected.
Essentially, for each step of the journey, you need to keep it self-contained in such a way that it doesn’t depend on the previous steps having particular outcomes.
Let’s say you want to use a plastic-type material in your product, whatever that might be. You’ll need a machine that can utilize that plastic. You’re favoring polyurethane and have a machine in mind that can use it.
So what do you put down in your roadmap? Get polyurethane. Then, get a working polyurethane machine. No, no, no, you don’t do that. ????
When placing the polyurethane machine into your roadmap, you’ve essentially condemned yourself to alter your roadmap if your plan of using polyurethane falls through.
What does this mean? Remember how I talked about efficiency and lines of communication? The team looking into obtaining machines for you isn’t necessarily going to be the same one testing the materials. If you’ve placed a polyurethane machine into your roadmap, you’re going to have them running around looking for a machine that is no longer practical for you.
That’s time, effort, and money wasted.
Long story short? Make your planning modular in the early stages, so you don’t run into these issues.
Stage #4: Parallel innovation processes
The process of utilizing a product development strategy can be a tough one. How are you supposed to tie a long-term strategy into your daily operations?
Well, there’s an answer to that, and it lies in parallel innovation processes.
The trick to doing both at once is tying them together. Sure, you can try and run your daily operations independently, but that’s just asking to be led astray.
The key lies in having two systems in place:
- A system for planning and budgeting in the long-term, often yearly.
- A system for the short-term to explore possibilities and select emerging concepts, often monthly.
So how do you tie them in? The outputs from your long-term process become your inputs for the short-term.
In other words, you use the data you’ve gathered from your long-term vision projections as the starting points for your short-term.
You might think to yourself, what’s the benefit of doing this? Well, short-term planning without long-term management can be misguided, and the most crucial aspect of all is the budget aspect.
Every year there might be millions of product concepts thought up. However, you can only continue onto the creation process if you have the budget and assets to do so.
You can’t have your cake and eat it too. ????
The parallel innovation process keeps you on track to create only those products you’re capable of creating. Whether it’s due to budget restraints, technological limits, or simply a lack of resources, keeping your overall goal tied to the present circumstances will ensure you stay grounded.
That’s not to say that you can’t pick up ideas later on when circumstances change. Avatar had to wait almost a decade for special effects technology to catch up to James Cameron’s vision. In the meantime, Cameron devoted his attention to other projects.
The takeaway? Stick to what you can feasibly do.
Conclusion
So there you have it! You should now have everything that you need to create a workable, useful, and reliable product development strategy.
What’s next?
Once your product is out there in people’s hands, they’re going to have things to say. It’s imperative you’ll learn how to collect this data, analyze it, and use it to create better products. Check out our customer feedback analysis article to understand what needs to be done.
 All
Articles
All
Articles Email
Analytics
Email
Analytics