
It is no secret knowing and understanding how and why consumers buy can make marketing a whole lot easier.
Sadly, we don’t have a crystal ball. But what we do have is Consumer Behavior analysis.
This article will explain what is Consumer Behavior, its importance, what influences consumers, and how you can leverage customer reviews to predict consumer trends and behaviors.
What is Consumer Behavior
Consumer behavior is the study of consumers and how they choose, use, and dispose of products and services. Essentially, It is a study of the actions and reasonings of consumers, an extensive look into what drives them to buy and use certain products.
Consumer buying behavior analysis studies incorporate ideas from multiple sciences, including psychology, biology, and economics, aiming to better understand and explain what consumers buy, why they buy, when they buy, how often they buy, and so on.
Importance of Consumer Behavior
Studying and understanding consumer behavior allows brands and marketing specialists to identify what influences consumers and their decisions.
Consumer behavior analysis helps:
- Identifying consumer pain points – mapping and explaining customers issues and difficulties with a brand, product, or service.
- Optimizing marketing efforts – understanding the best way to engage with consumers and convert them.
- Improve product and brand innovation – identifying what products or services consumers are missing in the current market, later using the data in product development or improvement.
But perhaps most importantly, consumer behavior analysis helps you understand what consumers think and feel about a brand, what influences them to choose one over the other, why and how they shop, and how their environment influences their behavior.
Types of Consumer Behavior
The four main types of consumer behavior are:
- Complex buying behavior – This type of behavior usually manifests when consumers are buying expensive, infrequently bought products (like a house or a car). In these situations, consumers tend to be very involved in the purchase process and conduct research before buying.
- Dissonance-reducing buying behavior – The consumer is highly involved but has difficulties determining the differences between brands, often worrying regretting their choice. Moreover, many consumers will seek outside confirmation they have made the right choice.
- Habitual buying behavior – In this kind of purchase, the consumer has very little involvement or sense of loyalty in the product or brand category. For example, when grocery shopping, most people will exhibit habitual patterns, not strong brand loyalty.
- Variety seeking behavior – In this scenario, consumers will buy a different product simply because they seek variety. They might be very pleased with the product they currently use, but want to change things up a bit.

Consumer Behavior Theory
The aforementioned behaviors and the marketing strategies tackling them, are based on
The psychological and economical study of human behavior, aka consumer behavior theory. Businesses use these theories to try and obtain a better understanding of their customers and market trends and shifts.
There are four major theories that seek to explain consumer behavior:
1. Theory of Reasoned Action (ToRA or TRA)
First created by Martin Fishbein and Icek Ajzen in the late 1960s, the Theory of Reasoned Action centers around the importance of people’s pre-existing attitudes in the decision-making process.
The core of the theory suggests that consumers are rational actors who choose to act in their best interests. Simply put, people will act based on their intention to generate a particular (usually favorable) outcome.
Hence, in order to serve their purpose, consumers are able and might change their mind and decide on a different course of action.
2. EKB (Engel, Kollet, Blackwell) Method
The EKB Model essentially expands the Theory of Reasoned Action, laying out a five-step process consumers use when making a purchase.
First, consumers absorb marketing on television, newspapers or online. After collecting the data, the consumer will move into information processing, comparing the input to past experiences and expectations.
Finally, after a period of thought, consumers move to the decision-making stage, where they will choose whether to make the purchase or not based on rational insight. In this final phase, consumers will be susceptible to process variables and external influences, like the desired final outcome or future plans.
3. Motivation-Need Theory
Psychologist Abraham Maslow first introduced his Hierarchy of Needs in 1943, forever changing the psychological community. As to Maslow’s theory, people act to fulfill their needs based on a five-part priority system – physiological (survival), safety, love, esteem, and self-actualization.
Later on, Business schools used Maslow’s theory to explain the need for tailoring marketing campaigns to consumers. Accordingly, successful marketing isn’t only about bringing awareness to a product, but also establishing it as a need for consumers.
4. Hawkins-Stern Impulse buying
Aiming to present a more complete picture of the average consumer, the Hawkins-Stern impulse buying theory combines rational action with impulse behavior. According to the theory, impulse purchases are driven by external stimuli, and have almost nothing to do with traditional decision-making.
Impulse buying theory specifies four categories of impulse buying – Purely impulse purchases, Reminded impulse buys, Suggested impulse purchases, and Planned impulse decisions.
Communicating and marketing to customers with these categories in mind can improve the chances consumers will choose to buy a product, even if they haven’t planned to do so in advance.
Factors Influencing Consumer Behavior
Consumer behavior is influenced by three major factors:
- Personal factors – Demographics (age, gender, culture, socio-economic status, etc.). For example, a person’s economic condition or purchasing power plays a big part in their decision making. A positive economic environment often makes consumers more confident and willing to indulge in more expensive or luxury products.
- Psychological factors – A person’s perceptions and attitudes. Consumer behavior is often influenced by a person’s set of perceptions, likes, dislikes, priorities, morals, and values.
- Social factors – Family, friends, social media. Peer pressure has a significant influence on consumer behavior. What our family members, classmates, neighbors, and acquaintances like, think, or do can play a major role in our decisions.

Consumer Behavior in eCommerce
Since most consumer behaviour theories were developed during the second half of the 20th century, they center around traditional store-shopping. But what happens when we take our shopping online?
It’s time to take a look at how e-commerce has changed consumer behavior.
Nowadays, most people in the US are doing their shopping online, preferring e-commerce platforms like Amazon, Shopify, and Target+ over traditional stores and shopping centers.
As a result, the way consumers shop has exponentially changed.
First and foremost, e-commerce has changed consumers’ expectations. Today’s consumers expect a seamless personalized shopping experience. Customer experience is required to be consistent (no matter what device they are using), engaging, and relevant. With 91% of consumers saying they are more likely to shop with brands that provide a customized and personalized experience, it’s something to take note of.
Secondly, shopping has become even more of a social activity.
With the explosion of social media over the past decade, it is only natural people would want to share their shopping experience with others. Digital marketing and online shopping platforms have made it easier for consumers to share their recent purchase or wish-list items, turning shopping into a social activity.
Moreover, consumers are actively researching, seeking and relying on others’ opinions and reviews.
According to a 2017 research by the Spiegel Research Centre, about 95% of people read customer reviews before making a purchase. Thanks to e-commerce platforms and social media, this task has become a piece of cake. Consumers have immediate, unlimited, and super-fast access to those reviews, with social platforms and online review sites a click away.
The bottom line is that along with the traditional consumer behavior, e-commerce era consumers are more social and connected – being more susceptible to those social factors, but at the same time able to do more research and tap into the rational aspect of decision making.
Consumer Behavior Research
A great way for businesses to adapt and optimize their marketing to this new and evolved consumer behavior, is by first understanding it. The best way to do so is by conducting consumer behavior research.
Much like market research, consumer behavior research requires data, and the more the merrier. Businesses collect and analyze information using different tools and solutions, like surveys, focus groups, keyword research, social listening, and more.
The data is collected and analysed with the aim of understanding and predicting consumer behavior, enabling brands to optimize their marketing campaigns, product innovation, and Go-To-Market (GTM) strategies.
Another tool companies use to try and predict consumer behavior is Consumer Behavior Modeling.
Consumer Behavior Modeling
Customer Behavior Modeling is the creation of a mathematical construct representing the common consumer’s behaviors in order to predict how similar customers will act.
Unfortunately, building customer behavior models is both a difficult and expensive task. They require skilled and trained personnel, that is not easy and cheap to come by.
But perhaps the most problematic aspect of Customer Behavior Modeling is that most customer models are simplistic, often ignoring many relevant factors, making their predictions incomplete and unreliable.
The solution to this issue is quite simply listening to the customers.
Consumer Behavior Examples
As formerly mentioned, there is always the option of surveying customers or using multiple focus groups to try and get the data required to predict consumer behavior.
However, there is a better, accessible and rich data source brands can leverage to predict consumer behavior – Customer Reviews.
Monitoring, collecting and analyzing consumer reviews helps businesses to find out what customers are saying about products or services, enabling them to predict trends and behaviors, potentially improving sales and earnings.
Revuze’s Topic analysis provides brands with a clear view of trending topics over time. For example, let’s take a look at the US Coffee Machine market. One of the major trends in this market segment is cold brew –
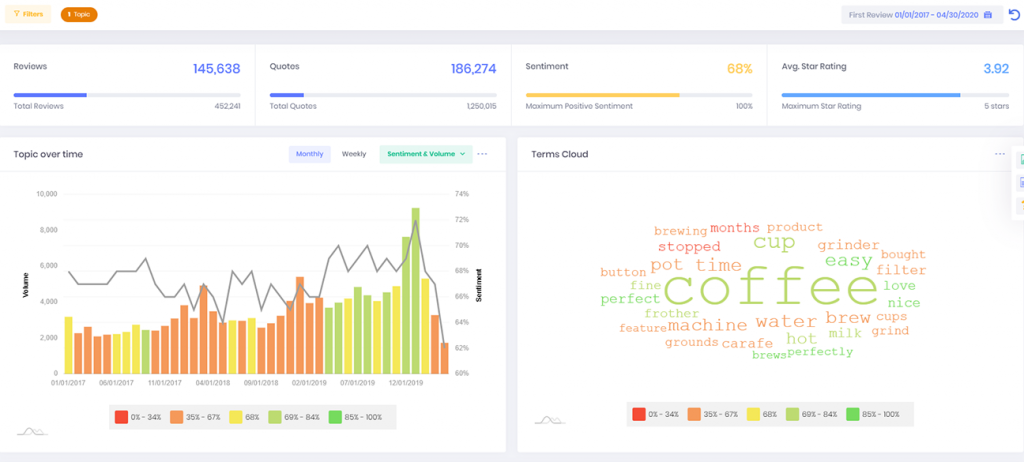
Over the past several years, cold brewed coffee has become a hit, especially with millennial consumers. Identifying the rising consumer interest allows brands to identify and react to market trends and consumer behaviour.
Revuze also provides customer reviews sentiment analysis, new reviews alert solution, and full industry reports, making sure brands won’t miss a beat.
Revuze’s Self learning algorithms scan and analyze customer reviews, identifying sentiment, flagging pain points, and detecting market trends. The end result is highly granular customer review analysis for data-driven decision making that will elevate your brand to a whole new level.
 All
Articles
All
Articles Email
Analytics
Email
Analytics








 Agencies
Insights
Agencies
Insights